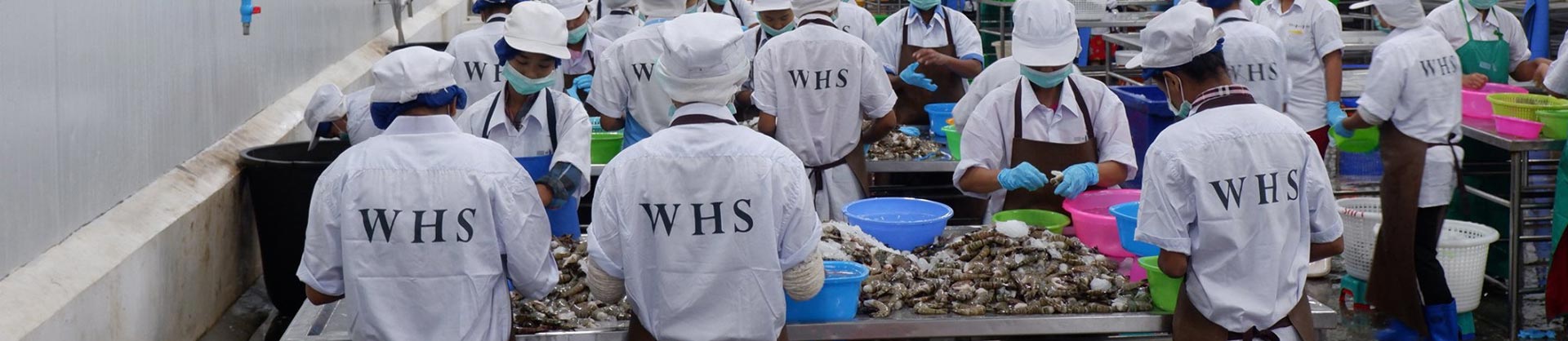
Myanmar Soft Shell Crab Market Condition in 2024
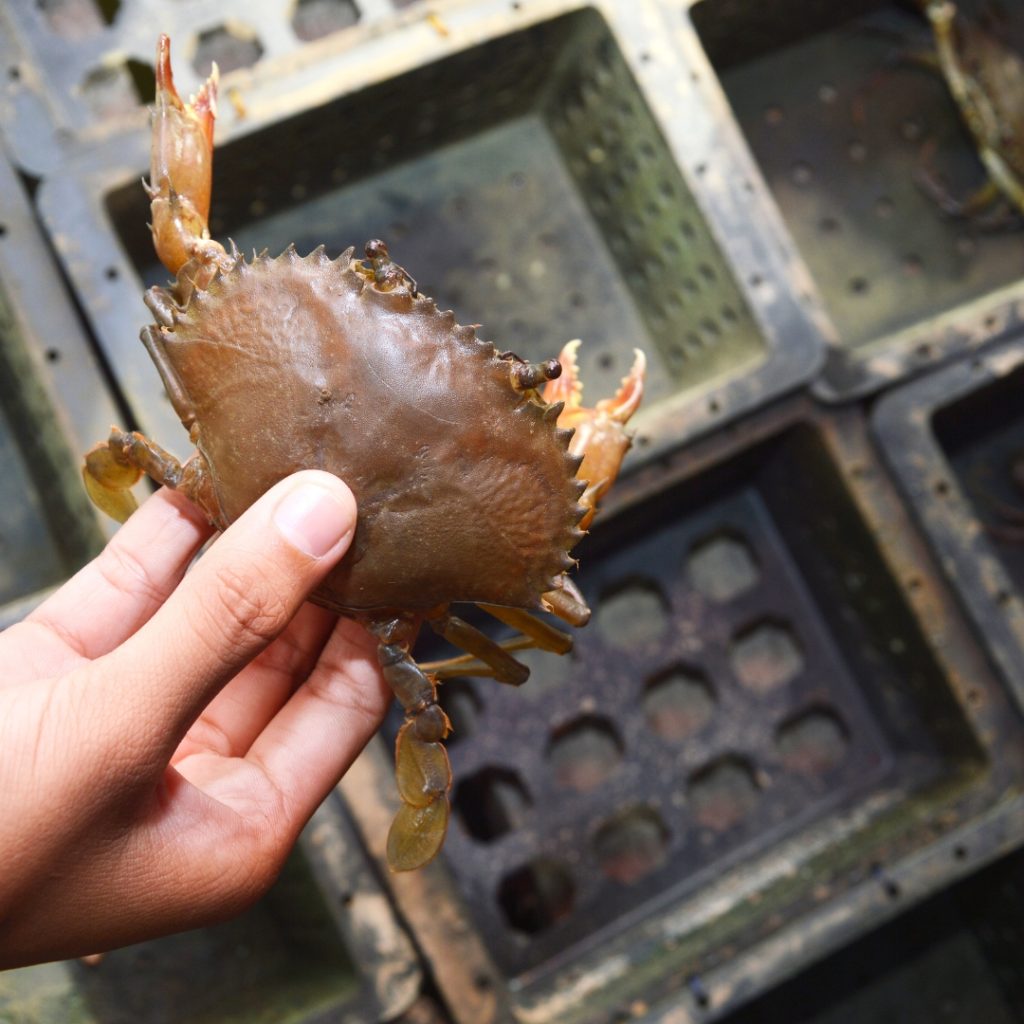

The soft-shell crab market in Myanmar in 2024 is experiencing a robust domestic demand, with the domestic market for soft-shell crabs being strong. The country’s soft-shell crab breeding and exports have seen significant growth, with the export volume reaching over $4.9 million in the fiscal year 2022-2023. Additionally, efforts are being made to increase the number of farming acres, with Rakhine State aiming to extend soft-shell crab farming to up to 500 acres.
However, the overall seafood market in Myanmar is facing a significant decrease in sales and product prices due to various factors. This decline may have an impact on the soft-shell crab market as well, although the domestic demand remains strong.
Despite the strong domestic demand for soft-shell crabs, the broader challenges in Myanmar’s seafood market could pose potential risks to the industry’s growth. Factors contributing to the overall decline in seafood sales and prices include economic instability, regulatory changes, and disruptions in supply chains due to global events or local circumstances.
The decline in the general seafood market might lead to increased competition among seafood producers, possibly affecting profit margins for soft-shell crab farmers. Additionally, any fluctuations in the availability and cost of resources necessary for soft-shell crab farming, such as feed and labour, could impact production costs and profitability.
To mitigate these risks, stakeholders in Myanmar’s soft-shell crab industry are likely to focus on several strategic initiatives. These may include:
- Diversification of Export Markets: By exploring new international markets and reducing reliance on a few key buyers, Myanmar can better insulate its soft-shell crab exports from global market fluctuations.
- Improvement of Farming Practices: Investing in advanced aquaculture technologies and sustainable farming practices can enhance productivity and reduce costs. This may involve the adoption of modern breeding techniques, better disease management, and improved feed efficiency.
- Value Addition: Developing value-added products such as processed or ready-to-cook soft-shell crab products can cater to changing consumer preferences and open up new market segments, both domestically and internationally.
- Strengthening Domestic Supply Chains: Enhancing the efficiency and reliability of domestic supply chains can ensure a steady supply of high-quality soft-shell crabs to meet strong local demand. This includes improving transportation, storage, and distribution networks.
- Government Support and Policy Advocacy: Engaging with the government to secure favourable policies and support for the seafood industry can help address some of the broader challenges. This might include seeking subsidies, tax incentives, or support for infrastructure development.
- Marketing and Branding: Promoting Myanmar’s soft-shell crabs through marketing campaigns that highlight their quality, sustainability, and uniqueness can help in building a strong brand presence in both domestic and international markets.
As Rakhine State and other regions expand their soft-shell crab farming areas, it will be crucial to balance this growth with sustainable practices to ensure long-term viability. Collaboration among farmers, exporters, government agencies, and industry associations will be key to navigating the current challenges and capitalizing on the opportunities in the soft-shell crab market.
By addressing these strategic areas, Myanmar’s soft-shell crab industry can continue to thrive despite the broader challenges in the seafood market, ensuring sustained growth and profitability in the years to come.